why, 为什么需要多路复用?
为什么要多路复用?,为什么引出多路复用。
对socket的I/O操作–》read,从I/O中得到数据, write,写数据到I/O中。
当没有多路复用,
- 我们操作
- 一个阻塞的socket,一个线程/进程只能操作一个,如果想要操作多个socket,那么就需要多个线程,
- 一个非阻塞socket,那么就需要用户代码一直轮训,消耗CPU。
1
2
3
| for i:= 0; i<len(sockets);i++{
read(sockets[i])
}
|
所以我们需要多路复用就是为了更加高效的操作多个非阻塞的流(socket)。
what,多路复用内部的原理
进程的调度。 ready,running,
硬件中断。
流的读写缓冲区,wake queue(唤醒队列)
当一个读或者写一个阻塞流的时候,如果没有数据可读,或者空间可写,那么这个线程或进程就会被CPU调度到非运行状态,且把这个线程/进程的标识放入这个流的wake queue里面,当这个流可读,或者空间可写的时候,把这个线程/进程标识为ready状态,放入CPU调度队列
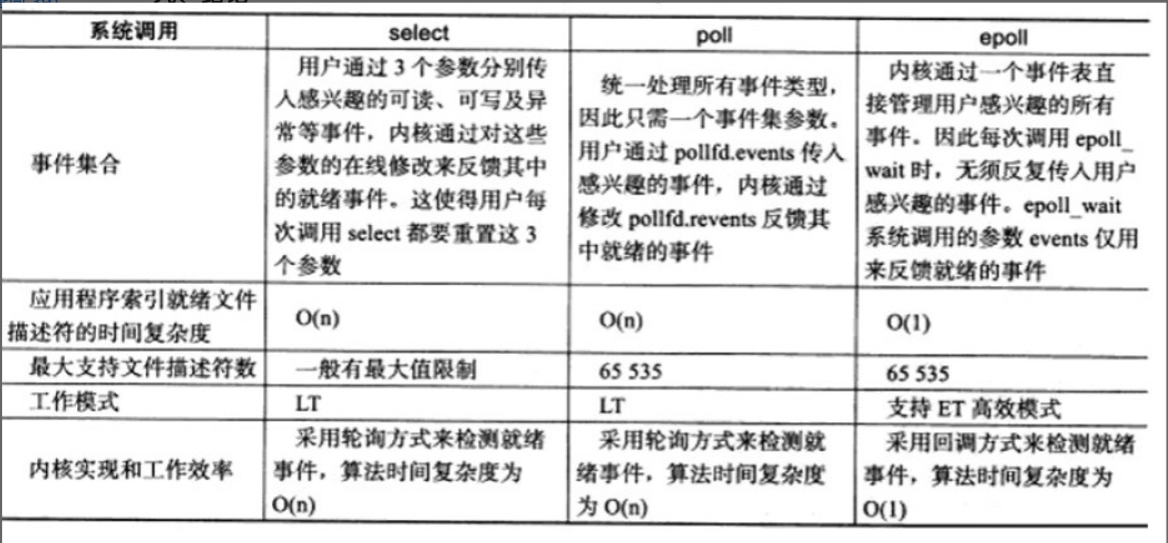
select
很容易就想到,当调用select的时候可以,把需要操作的流和对应事件从用户空间,传入内核空间,
epoll/kqueue
去掉每次都要传递流的文件描述符和对应事件给内核的步骤,epoll/kqueue独立出来一个系统函数,来管理需要操作流文件描述符,和对应的事件。(epoll_ctl(), kevent())
当阻塞的时候,让流的wake queue关联的是epoll/kqueue的文件描述符,而不是线程/进程。
当流有事件发生,通知到epoll/kqueue的结构体上去。
使用epoll/kqueue做中介,当epoll_wait(),直接得出当前关注的流中是否有事件发生
int kqueue(void);
int kevent(int kq,
const struct kevent *changelist, int nchanges,
struct kevent *eventlist, int nevents,
const struct timespec *timeout);
从这个系统函数可以看出,epoll和kqueue应该没有文件描述符限制。
how,如何使用多路复用
当同时存在changelist/nchange,与eventlist/nevent,kqueue总是先判断nchange是否大于0,然后先应用changelist,然后再读已经pending event.
- All changes contained in the changelist are applied before any pending events are read from the queue.
kqueue source code
wiki

先来一个当changelist改变的时候,eventlist返回中会不会有它
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
| #include <sys/event.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h> /* for strerror() */
#include <unistd.h>
/* function prototypes */
void diep(const char *s);
int main(void)
{
struct kevent change[3]; /* event we want to monitor */
struct kevent event[3]; /* event that was triggered */
pid_t pid;
int kq, nev;
struct kevent *changelist = change;
int nchanges = 1;
/* create a new kernel event queue */
if ((kq = kqueue()) == -1)
diep("kqueue()");
/* initalise kevent structure */
EV_SET(&change[0], 1, EVFILT_TIMER, EV_ADD | EV_ENABLE, 0, 6000, 0);
EV_SET(&change[1], 2, EVFILT_TIMER, EV_ADD | EV_ENABLE, 0, 3000, 0);
/* loop forever */
int count = 0;
for (;;) {
nev = kevent(kq, changelist, nchanges, &event[0], 3, NULL);
if (nev < 0)
diep("kevent()");
else if (nev > 0) {
for(int i=0; i<nev; i++){
printf("\n\n------------begin--number[%d]---------------------\n", nev);
if (event[i].flags & EV_ERROR) { /* report any error */
fprintf(stderr, "EV_ERROR: %s\n", strerror(event[i].data));
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if ((pid = fork()) < 0) /* fork error */
diep("fork()");
else if (pid == 0) /* child */{
printf("\tisChild pid[%d]\r\n", pid);
if (execlp("date", "date", (char *)0) < 0)
diep("execlp()");
}else{
printf("\tisFather pid[%d];event.ident[*%d*];count[%d];----;nchanges[%d];changelist[%p] \r\n", pid, event[i].ident, count, nchanges, changelist);
if(count==2){ // --------------here,当执行了0,1,2三次后,改变changelist,增加一个新的定时器,
nchanges = 1;
changelist = &change[1];
}
count++;
}
}
}
}
close(kq);
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
void diep(const char *s)
{
perror(s);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
//下面是输出
/Users/9dwit/codeing/untitled1/cmake-build-debug/untitled1
------------begin--number[1]---------------------
isFather pid[24203];event.ident[*1*];count[0];----;nchanges[1];changelist[0x7ffee67f67e0]
isChild pid[0]
Wed Oct 28 15:57:36 CST 2020
------------begin--number[1]---------------------
isFather pid[24204];event.ident[*1*];count[1];----;nchanges[1];changelist[0x7ffee67f67e0]
isChild pid[0]
Wed Oct 28 15:57:42 CST 2020
------------begin--number[1]---------------------
isFather pid[24205];event.ident[*1*];count[2];----;nchanges[1];changelist[0x7ffee67f67e0]
isChild pid[0]
Wed Oct 28 15:57:48 CST 2020
------------begin--number[1]---------------------
isFather pid[24206];event.ident[*2*];count[3];----;nchanges[1];changelist[0x7ffee67f6800] //------------here,这里出现了,它是立即生效的
isChild pid[0]
Wed Oct 28 15:57:51 CST 2020
------------begin--number[1]---------------------
isFather pid[24207];event.ident[*1*];count[4];----;nchanges[1];changelist[0x7ffee67f6800]
isChild pid[0]
Wed Oct 28 15:57:54 CST 2020
------------begin--number[1]---------------------
isFather pid[24208];event.ident[*2*];count[5];----;nchanges[1];changelist[0x7ffee67f6800]
isChild pid[0]
Wed Oct 28 15:57:57 CST 2020
|
这里要特别注意,如果changelist一直没改变,它会一直reset,可能会导致它永远不会触发
只改动一行,上面的就一直不会出现了。 EV_SET(&change[1], 2, EVFILT_TIMER, EV_ADD | EV_ENABLE, 0, 3000, 0); —> EV_SET(&change[1], 2, EVFILT_TIMER, EV_ADD | EV_ENABLE, 0, 7000, 0);
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
| /Users/9dwit/codeing/untitled1/cmake-build-debug/untitled1
------------begin--number[1]---------------------
isFather pid[25159];event.ident[*1*];count[0];----;nchanges[1];changelist[0x7ffee11177e0]
isChild pid[0]
Wed Oct 28 16:12:01 CST 2020
------------begin--number[1]---------------------
isFather pid[25160];event.ident[*1*];count[1];----;nchanges[1];changelist[0x7ffee11177e0]
isChild pid[0]
Wed Oct 28 16:12:07 CST 2020
------------begin--number[1]---------------------
isFather pid[25161];event.ident[*1*];count[2];----;nchanges[1];changelist[0x7ffee11177e0]
isChild pid[0]
Wed Oct 28 16:12:13 CST 2020
------------begin--number[1]---------------------
isFather pid[25163];event.ident[*1*];count[3];----;nchanges[1];changelist[0x7ffee1117800]
isChild pid[0]
Wed Oct 28 16:12:19 CST 2020
------------begin--number[1]---------------------
isFather pid[25164];event.ident[*1*];count[4];----;nchanges[1];changelist[0x7ffee1117800]
isChild pid[0]
Wed Oct 28 16:12:25 CST 2020
------------begin--number[1]---------------------
isFather pid[25167];event.ident[*1*];count[5];----;nchanges[1];changelist[0x7ffee1117800]
isChild pid[0]
Wed Oct 28 16:12:31 CST 2020
------------begin--number[1]---------------------
isFather pid[25169];event.ident[*1*];count[6];----;nchanges[1];changelist[0x7ffee1117800]
isChild pid[0]
Wed Oct 28 16:12:37 CST 2020
------------begin--number[1]---------------------
isFather pid[25170];event.ident[*1*];count[7];----;nchanges[1];changelist[0x7ffee1117800]
isChild pid[0]
Wed Oct 28 16:12:43 CST 2020
Process finished with exit code 15
|
所以changelist可以和eventlist混合用,但是changlist使用完后,一定要把上次的改变移除,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
| #include <sys/event.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h> /* for strerror() */
#include <unistd.h>
/* function prototypes */
void diep(const char *s);
int main(void)
{
struct kevent change[3]; /* event we want to monitor */
struct kevent event[3]; /* event that was triggered */
pid_t pid;
int kq, nev;
struct kevent *changelist = change;
int nchanges = 1;
/* create a new kernel event queue */
if ((kq = kqueue()) == -1)
diep("kqueue()");
/* initalise kevent structure */
EV_SET(&change[0], 1, EVFILT_TIMER, EV_ADD | EV_ENABLE, 0, 2000, 0);
EV_SET(&change[1], 2, EVFILT_TIMER, EV_ADD | EV_ENABLE, 0, 3000, 0);
EV_SET(&change[2], 3, EVFILT_TIMER, EV_ADD | EV_ENABLE, 0, 4000, 0);
/* loop forever */
int count = 0;
for (;;) {
nev = kevent(kq, changelist, nchanges, &event[0], 3, NULL);
if (nev < 0)
diep("kevent()");
else if (nev > 0) {
for(int i=0; i<nev; i++){
if (event[i].flags & EV_ERROR) { /* report any error */
fprintf(stderr, "EV_ERROR: %s\n", strerror(event[i].data));
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if ((pid = fork()) < 0) /* fork error */
diep("fork()");
else if (pid == 0) /* child */{
printf("\tisChild pid[%d]\r\n", pid);
if (execlp("date", "date", (char *)0) < 0)
diep("execlp()");
//nchanges = 0;
}else{
printf("\tisFather pid[%d];event.ident[%d];count[%d];----;nchanges[%d];changelist[%p] \r\n", pid, event[i].ident, count, nchanges, changelist);
if(count==3 && event[i].ident ==1){
nchanges = 1;
changelist = &change[1];
//changelist = NULL;
//changelist = &change[0];
//EV_SET(&change[0], 1, EVFILT_TIMER, EV_DISABLE, 0, 3000, 0);
}else if(count==5){
nchanges = 1;
changelist = &change[2];
}else if(count==10) {
nchanges = 0;
changelist = NULL;
}
/* //else if(count == 6){
//else if(count == 0 || count == 5){
//else{
nchanges = 0;
changelist = NULL;
}else if(count == 7){
//nchanges = 1;
//changelist = &change[1];
nchanges = 1;
changelist = &change[0];
}*/
count++;
}
}
}
}
close(kq);
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
void diep(const char *s)
{
perror(s);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
|
附录
流的概念,
- 一个流可以是文件,socket,pipe等等可以进行I/O操作的内核对象。不管是文件,还是套接字,还是管道,我们都可以把他们看作流。
I/O的操作,
- 通过read,我们可以从流中读入数据;通过write,我们可以往流写入数据。
kqueue APIs
epoll
FreeBSD Kqueue的实现原理
Epoll 新增 EPOLLEXCLUSIVE 选项解决了新建连接的’惊群‘问题

